Renin Angiotensin System Flow Chart
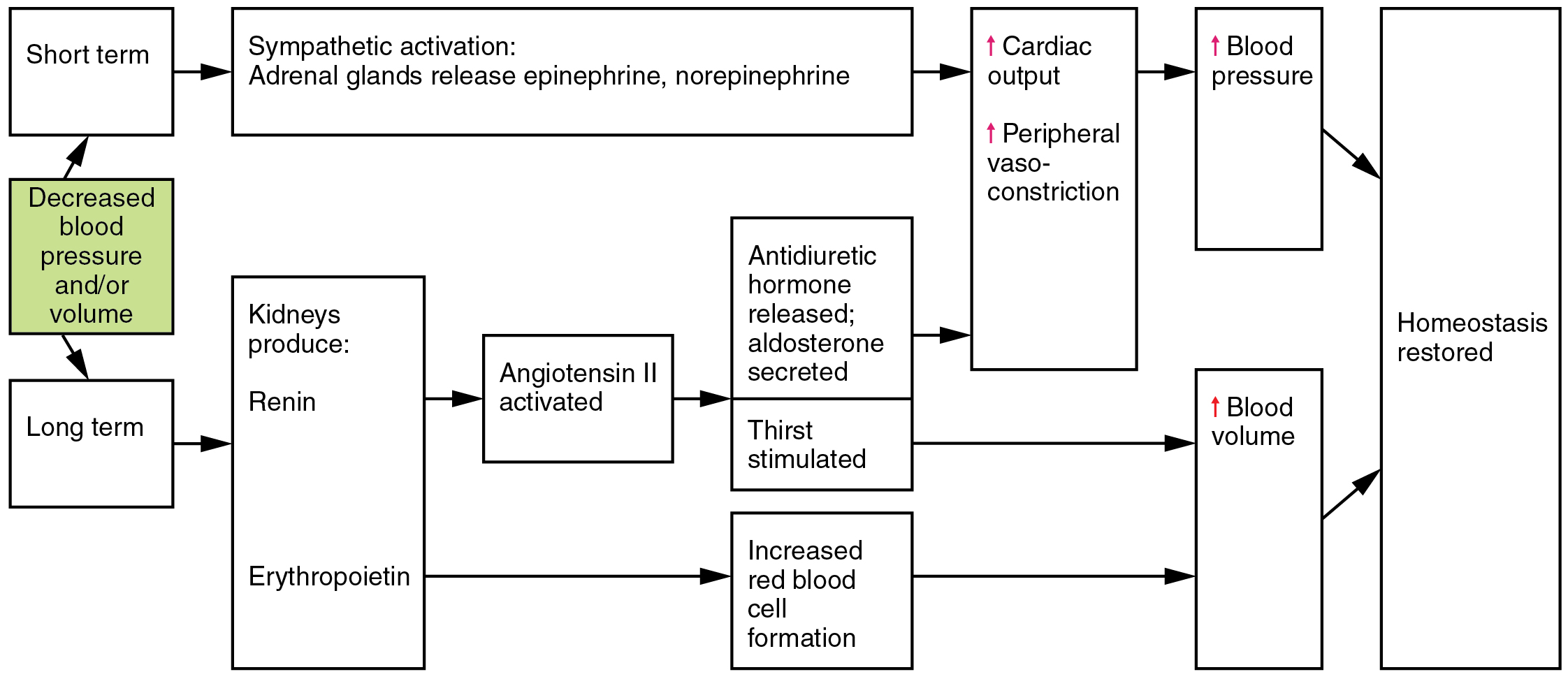
Renin Angiotensin System Flow Chart. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is a critical regulator of blood volume and systemic vascular resistance. The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is a group of related hormones that act together to regulate blood pressure and control inflammation.

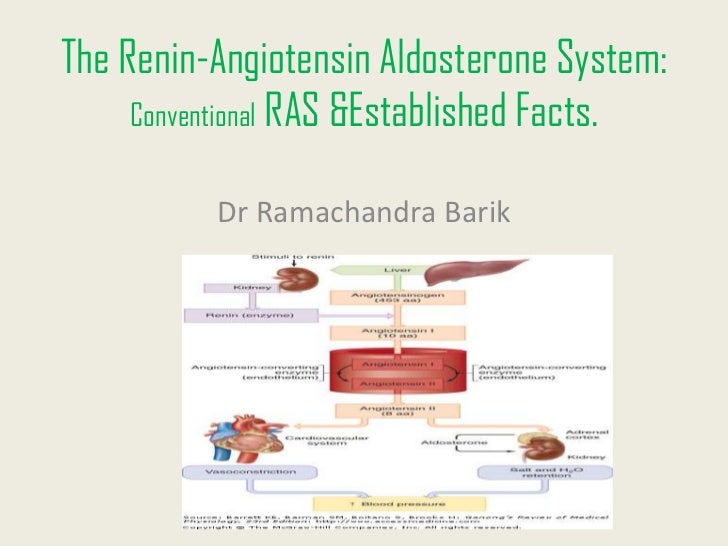
Angiotensin II also causes the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) which functions to conserve water in the body when volume is low; it does this by inserting.
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is a central element in the control of the salt and water balance of the body and arterial blood pressure.
In the event of blood pressure dropping, renin is secreted due to the decreased stretch of the juxtaglomerular cells and an increased sympathetic stimulation, triggered by the decreased activation of arterial baroreceptors. Renin is an enzyme secreted into the blood from specialized cells that encircle the arterioles at the entrance to the glomeruli of the kidneys (the renal capillary networks that are the filtration units of the kidney). The renin-angiotensin system (RAS), or renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance.






Comments
Post a Comment